Phase to ground voltage refers to the voltage difference between any phase conductor and the ground. It’s crucial for ensuring safe electrical system operations.
Phase to ground voltage is a fundamental concept in electrical engineering. It represents the potential difference between a live conductor and the earth. This voltage is vital for the safety and functionality of electrical systems. Understanding it helps in preventing electrical hazards and ensuring efficient power distribution.
Electricians and engineers regularly measure this voltage to maintain system integrity. Accurate measurements can prevent equipment damage and ensure the safety of personnel. By understanding phase to ground voltage, you can maintain a reliable and safe electrical environment. This knowledge is essential for anyone involved in electrical installations or maintenance.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Introduction To Phase To Ground Voltage
Understanding Phase to Ground Voltage is crucial for anyone involved in electrical systems. This voltage plays a key role in ensuring safety and efficiency. Let’s dive into the basic concepts and why it’s important.
Basic Concept
Phase to Ground Voltage refers to the voltage measured between a phase conductor and the ground. It is a fundamental aspect of electrical engineering.
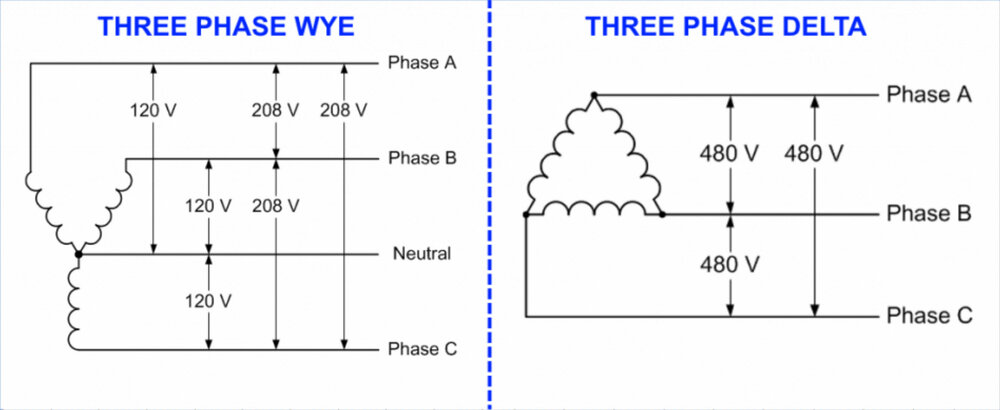
In a three-phase system, this measurement helps assess the system’s balance and safety. The voltage can vary depending on the system configuration, such as star or delta.
Here is a simple comparison:
| System | Phase to Phase Voltage | Phase to Ground Voltage |
|---|---|---|
| Star (Wye) | 400V | 230V |
| Delta | 400V | N/A |
Importance In Electrical Systems
Phase to Ground Voltage is vital for safety and equipment operation. It helps in detecting faults and ensuring the system runs smoothly.
A proper understanding can prevent electrical hazards and reduce downtime. This knowledge is essential for electricians, engineers, and anyone working with electrical systems.
Consider these key points:
- Helps in fault detection
- Ensures system balance
- Prevents electrical hazards
- Optimizes equipment performance
Measuring Techniques
Understanding Phase to Ground Voltage is crucial for electrical safety. Accurate measurement ensures safe operation. This section delves into the best techniques for measuring Phase to Ground Voltage.
Tools Required
- Digital Multimeter
- Insulated Gloves
- Insulated Footwear
- Safety Goggles
- Test Leads
Step-by-step Guide
- Ensure all safety gear is worn.
- Set the digital multimeter to AC voltage.
- Insert test leads into the multimeter.
- Connect the black lead to the ground.
- Connect the red lead to the phase wire.
- Read the voltage display on the multimeter.
- Note the reading for future reference.
Following these steps ensures an accurate reading. Safety is paramount when dealing with electrical measurements.
Common Hazards
Understanding the common hazards associated with phase to ground voltage is crucial. These hazards pose risks to both people and equipment. Addressing these risks can prevent accidents and equipment failures.
Electrical Shock
Electrical shock is a serious hazard of phase to ground voltage. It occurs when a person touches a live wire. This can cause severe injury or even death. The severity depends on the voltage and duration of contact.
- Direct contact with live wires
- Improper insulation
- Faulty wiring
To reduce the risk of electrical shock, follow these safety measures:
- Use proper insulation materials.
- Regularly inspect and maintain electrical systems.
- Wear protective gear when handling live wires.
Equipment Damage
Phase to ground voltage can also cause equipment damage. Electrical surges can lead to malfunction or complete failure. This can result in costly repairs or replacements.
| Cause | Effect |
|---|---|
| Electrical surges | Malfunction or failure |
| Improper grounding | Short circuits |
| Faulty components | Reduced lifespan |
To prevent equipment damage, consider these tips:
- Ensure proper grounding of all equipment.
- Use surge protectors.
- Regularly inspect and replace faulty components.
Credit: www.electriciansjournal.com
Safety Precautions
Understanding phase to ground voltage is crucial for electrical safety. Following proper safety precautions can prevent accidents and injuries. Below are key safety measures to consider.
Protective Gear
Wearing the right protective gear is essential. This includes insulated gloves, safety goggles, and hard hats. These items protect against electrical shocks and flying debris.
- Insulated gloves protect your hands from electrical currents.
- Safety goggles shield your eyes from sparks.
- Hard hats protect your head from falling objects.
Always inspect your gear for damage before use. Replace any worn or damaged items immediately. Proper maintenance ensures maximum protection.
Safe Work Practices
Adhering to safe work practices minimizes risks. Follow these guidelines:
- Always turn off the power before working on electrical circuits.
- Use a voltage tester to confirm circuits are de-energized.
- Maintain a safe distance from high-voltage lines.
- Keep tools and equipment in good condition.
- Work in a dry environment to avoid electrical conductivity.
Using a voltage tester ensures that circuits are safe to touch. Keeping tools in good condition prevents accidental shorts.
Remember, safety should always come first. Adhering to these precautions can save lives and prevent injuries.
Regulatory Standards
Understanding regulatory standards for Phase to Ground Voltage is crucial. These standards ensure safety and compliance. They differ across countries and regions. This section covers both national codes and international guidelines.
National Codes
Every country has its own set of national codes. These codes regulate Phase to Ground Voltage to ensure safety.
| Country | Regulatory Body | Standard Code |
|---|---|---|
| United States | National Electrical Code (NEC) | NEC 110.4 |
| Canada | Canadian Electrical Code (CEC) | CEC Section 10 |
| United Kingdom | British Standards Institution (BSI) | BS 7671 |
International Guidelines
Beyond national codes, international guidelines also play a role. These guidelines help standardize practices across borders.
- IEC 60038: Defines standard voltages globally.
- IEEE Std 142: Provides grounding practices.
- ISO/IEC 30129: Covers high-voltage installations.
These guidelines ensure Phase to Ground Voltage compliance worldwide. They promote safety and interoperability.

Credit: m.youtube.com
Troubleshooting Issues
Phase to ground voltage issues can disrupt electrical systems. Proper troubleshooting ensures safety and functionality. This section guides you on identifying problems and finding effective solutions.
Identifying Problems
Start by measuring the voltage between the phase and ground. Use a reliable multimeter.
- If the reading is zero, there might be a ground fault.
- High readings indicate a possible open ground.
- Fluctuating readings suggest loose connections.
Inspect wires and connections visually. Look for signs of damage or wear.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Visual Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Zero Voltage | Ground Fault | Burnt marks |
| High Voltage | Open Ground | Disconnected wires |
| Fluctuating Voltage | Loose Connection | Loose terminals |
Effective Solutions
Once problems are identified, apply effective solutions:
- Ground Fault: Replace damaged wires. Ensure proper insulation.
- Open Ground: Reconnect any disconnected wires. Test the ground integrity.
- Loose Connection: Tighten all terminals and screws. Use appropriate tools.
Always retest the system after making adjustments. Ensure stable and correct voltage readings.
Regular maintenance can prevent phase to ground voltage issues. Check connections and insulation periodically.
Case Studies
Understanding Phase to Ground Voltage involves real-world applications. This section examines how it affects different scenarios. Let’s look at some case studies to see its impact.
Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, Phase to Ground Voltage plays a crucial role. A stable voltage ensures smooth operations. Here are some examples:
- Manufacturing Plants: Machines often run on three-phase power. Consistent voltage prevents equipment damage.
- Data Centers: Servers need reliable power. Phase to Ground Voltage ensures data integrity.
- Chemical Plants: Safety is paramount. Proper voltage levels reduce the risk of electrical hazards.
| Industry | Phase to Ground Voltage Impact |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Protects machinery from voltage spikes. |
| Data Centers | Ensures reliable server performance. |
| Chemical Plants | Reduces risk of electrical hazards. |
Residential Scenarios
In residential areas, Phase to Ground Voltage affects everyday life. Understanding its impact helps in maintaining electrical safety. Let’s explore some examples:
- Home Appliances: Voltage levels affect their performance. Stable voltage extends appliance life.
- Lighting Systems: Consistent voltage ensures proper lighting. Flickering lights often indicate voltage issues.
- Home Offices: Reliable voltage is crucial. It protects sensitive equipment like computers.
| Residential Area | Phase to Ground Voltage Impact |
|---|---|
| Home Appliances | Improves performance and longevity. |
| Lighting Systems | Ensures steady and reliable lighting. |
| Home Offices | Protects sensitive electronic equipment. |
Future Trends
The electrical industry is evolving rapidly. Understanding future trends in Phase to Ground Voltage is crucial. These trends are driven by technological advancements and the need for improved safety.
Technological Advancements
New technologies are making phase to ground voltage systems more efficient. Here are some key advancements:
- Smart Grids: These grids use digital technology to improve reliability.
- IoT Integration: Internet of Things (IoT) helps in real-time monitoring.
- Advanced Sensors: New sensors provide accurate voltage measurements.
- Energy Storage: Better batteries help in managing voltage spikes.
Improved Safety Measures
Safety is a top priority in electrical systems. New safety measures are enhancing protection against faults. Key improvements include:
- Automated Systems: Automation reduces human error.
- Enhanced Insulation: Better materials reduce leakage risks.
- Ground Fault Indicators: These devices quickly detect faults.
- Protective Relays: These relays ensure rapid response to faults.
| Advancements | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Smart Grids | Increased reliability |
| IoT Integration | Real-time monitoring |
| Advanced Sensors | Accurate measurements |
| Energy Storage | Better voltage management |
These trends are shaping the future of phase to ground voltage systems. Staying updated on these changes is crucial for industry professionals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Voltage Between Phase And Ground?
The voltage between phase and ground typically measures around 120V in the US and 230V in Europe. Always verify local standards.
What Is The Voltage To Ground For 480v 3-phase Phase?
The voltage to ground for a 480V 3-phase system is typically 277V. This is derived from the phase-to-phase voltage divided by the square root of three.
How Do You Calculate Phase To Ground Voltage?
To calculate phase to ground voltage, divide the line voltage by the square root of 3 (approximately 1. 732). For example, if the line voltage is 480V, the phase to ground voltage is 480V / 1. 732, which equals about 277V.
This formula applies to three-phase systems.
What Should Phase To Ground Be?
Phase to ground voltage should typically be 120V in a standard residential system. Always consult local electrical codes.
Conclusion
Understanding phase to ground voltage is crucial for electrical safety and system efficiency. Accurate measurements prevent potential hazards. Regular maintenance and checks ensure optimal performance. Stay informed and prioritize safety to avoid electrical issues. Embrace proper practices to maintain the integrity of your electrical systems.
