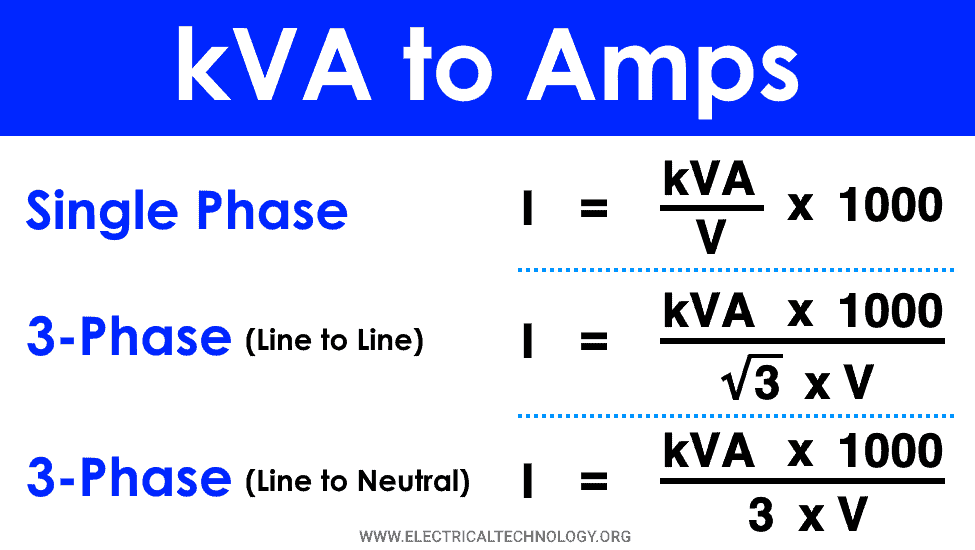
To convert kVA to Amps, divide the kVA by the voltage and multiply by 1,000. This formula applies to single-phase systems.
Understanding electrical conversions is crucial for managing power systems efficiently. KVA (kilovolt-amperes) measures apparent power, while Amps measure current. Converting between these units helps ensure that electrical systems operate within safe limits. Knowing the relationship between kVA and Amps aids in selecting appropriate equipment and avoiding overloads.
This knowledge is particularly important for electricians, engineers, and anyone involved in electrical installations. Accurate conversions enhance system reliability and performance. Therefore, mastering these conversions is essential for optimal electrical system management.
Introduction To Electrical Conversions
Electrical conversions are essential in many applications. They are used in both industrial and residential settings. One crucial conversion is from kVA to Amps. This conversion helps in determining the current needed for specific electrical devices.
Importance Of Accurate Conversions
Accurate conversions ensure safety and efficiency. Incorrect conversions can lead to device failures. They may also cause electrical hazards.
Correctly converting kVA to Amps helps in proper sizing of electrical components. It ensures that wires and circuits can handle the required load.
Common Conversion Challenges
Many face challenges with electrical conversions. One common issue is understanding the formulas.
Converting kVA to Amps involves knowing the voltage. The formula changes based on whether the circuit is single-phase or three-phase.
| Type of Circuit | Formula |
|---|---|
| Single-Phase | Amps = (kVA 1000) / Voltage |
| Three-Phase | Amps = (kVA 1000) / (Voltage √3) |
Another challenge is voltage variation. Voltage levels can vary in different regions. This affects the accuracy of conversions.
- Always use the correct voltage value.
- Double-check calculations for accuracy.
- Use reliable tools and software.
Understanding these challenges can help achieve precise electrical conversions. This ensures safe and efficient electrical systems.
Credit: www.bigrentz.com
Understanding Kva And Amps
Many people find electrical terms confusing. Two common terms are kVA and Amps. Both are essential in electrical systems. This section will help you understand these terms better.
Definition Of Kva
kVA stands for kilovolt-amperes. It is a unit of apparent power. It is used in electrical circuits. kVA combines volts and amperes. It measures the total power in a system. This includes both real power and reactive power. Real power does actual work, like lighting a bulb. Reactive power maintains the electric and magnetic fields. Understanding kVA helps in choosing the right equipment.
Definition Of Amps
Amps stands for amperes. It measures the flow of electrical current. Think of it as the amount of electricity flowing through a wire. More amps mean more current. Amps are crucial for determining wire sizes and circuit breakers. Knowing amps helps in preventing electrical overloads.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| kVA | Kilovolt-amperes, unit of apparent power |
| Amps | Amperes, measures flow of electrical current |
Understanding both kVA and amps is vital. It ensures safe and efficient electrical systems.
The Relationship Between Kva And Amps
Understanding the relationship between kVA and Amps is essential. Many applications involve converting power units. This knowledge is crucial for electricians, engineers, and students. The conversion process involves formulas and key factors. This section will help you grasp these concepts easily.
Basic Conversion Formula
The basic conversion formula is straightforward. It involves knowing the voltage. Use this simple formula:
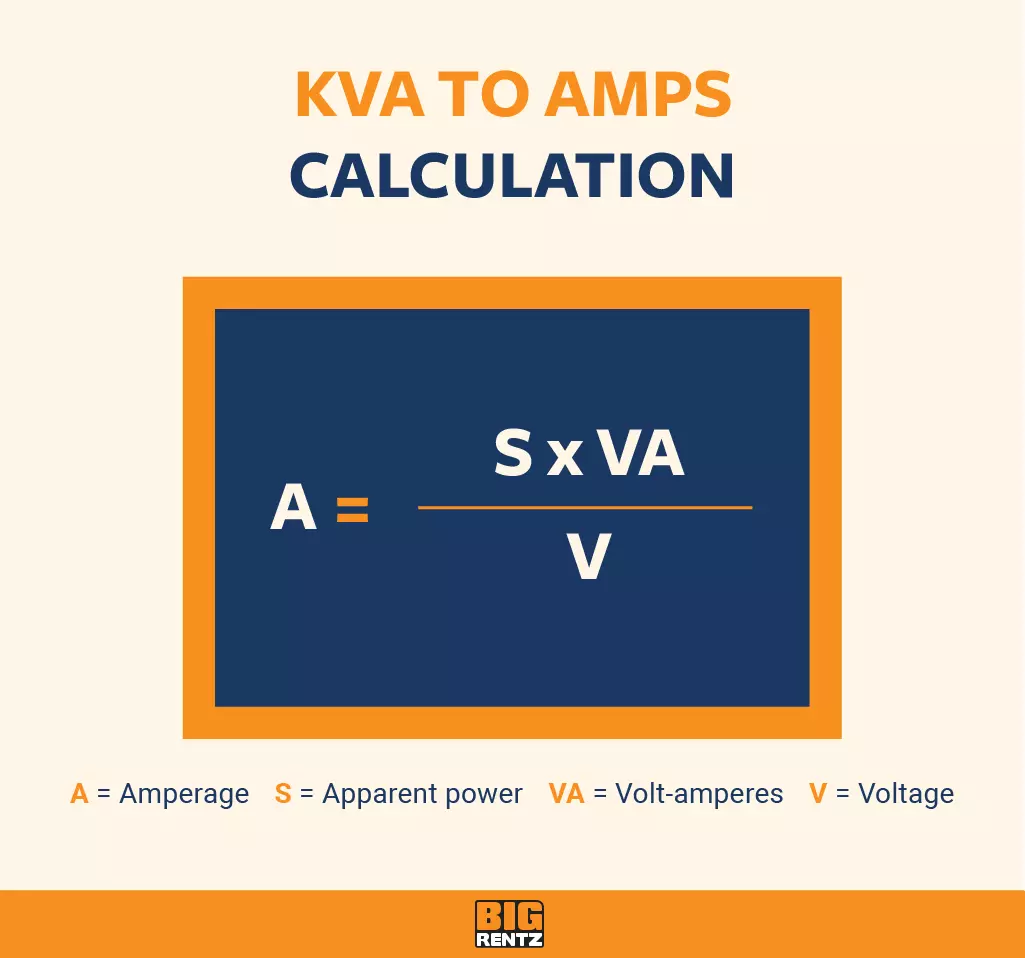
Amps = kVA × 1000 / VoltageThis formula helps in converting kVA to Amps. Remember, always use the correct voltage value.
Factors Affecting Conversion
Several factors affect the conversion. These include:
- Voltage type: AC or DC voltage impacts the result.
- Power factor: Especially important in AC circuits.
- Load type: Resistive or inductive loads also matter.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Voltage Type | AC or DC voltage changes the conversion. |
| Power Factor | Influences the conversion in AC circuits. |
| Load Type | Resistive or inductive loads affect the outcome. |
Understanding these factors can help in accurate conversions. Always consider them during calculations.

Credit: www.electricaltechnology.org
Step-by-step Conversion Process
Converting Kva into Amp is simple. Follow our step-by-step guide. You will understand the necessary variables and apply the conversion formula easily.
Identify Necessary Variables
Before starting, identify the following variables:
- Kva – Kilovolt-amps, a unit of apparent power.
- Voltage – The voltage in volts (V).
- Power Factor – Usually between 0 and 1.
These variables are essential for accurate conversion. Gather them before proceeding.
Apply The Conversion Formula
Use the formula to convert Kva to Amp:
Amp = (Kva 1000) / (Voltage Power Factor)Follow these steps:
- Multiply Kva by 1000.
- Multiply Voltage by Power Factor.
- Divide the result from step 1 by the result from step 2.
Here’s an example:
| Kva | Voltage (V) | Power Factor | Amp (A) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 400 | 0.8 | 31.25 |
In this example, 10 Kva is converted to 31.25 Amps.
Practical Examples
Understanding how to convert kVA into Amps can be very useful. This section provides practical examples for both single-phase and three-phase systems. These examples will help you grasp the concept easily.
Single-phase Example
For a single-phase system, the formula to convert kVA to Amps is:
Amps = (kVA × 1000) / VoltsLet’s consider a practical example. Assume you have a 5 kVA load running on a 240V single-phase supply. Using the formula:
Amps = (5 kVA × 1000) / 240V = 5000 / 240 = 20.83 AmpsSo, a 5 kVA load requires 20.83 Amps at 240V.
Three-phase Example
For a three-phase system, the formula to convert kVA to Amps is:
Amps = (kVA × 1000) / (√3 × Volts)Let’s consider a practical example. Assume you have a 10 kVA load running on a 400V three-phase supply. Using the formula:
Amps = (10 kVA × 1000) / (√3 × 400V) = 10000 / 692.82 = 14.44 AmpsSo, a 10 kVA load requires 14.44 Amps at 400V.
Here’s a quick reference table for different values:
| kVA | Volts | Single-Phase Amps | Three-Phase Amps |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 240 | 20.83 | 7.21 |
| 10 | 400 | 25.00 | 14.44 |
| 15 | 480 | 31.25 | 18.08 |
Use these practical examples and table to quickly convert kVA to Amps. It simplifies your calculations and helps in real-world applications.
Tools And Calculators
Understanding how to convert KVA into Amps can be tricky. Luckily, several tools and calculators can help. These tools make the conversion process easy and quick. This section covers various tools and methods you can use.
Online Conversion Tools
Online conversion tools simplify the KVA to Amps conversion. These tools are user-friendly and provide instant results.
- Enter the KVA value.
- Choose the phase type: single-phase or three-phase.
- Input the voltage.
- Press the calculate button.
Within seconds, you get the Amps value. These tools are accurate and save time.
Manual Calculation Methods
Manual calculation methods are also reliable. You can perform the conversion using simple formulas.
| Formula | Explanation |
|---|---|
| A = (KVA 1000) / V | Where A is Amps, KVA is kilovolt-amperes, V is voltage. |
Example: For a 5 KVA system with 240V, A = (5 1000) / 240 = 20.83 Amps.
| Formula | Explanation |
|---|---|
| A = (KVA 1000) / (1.732 V) | Where A is Amps, KVA is kilovolt-amperes, V is voltage, 1.732 is the square root of 3. |
Example: For a 10 KVA system with 400V, A = (10 1000) / (1.732 400) = 14.43 Amps.
Both methods help you get accurate results. Choose the one that suits you best.
Common Mistakes To Avoid
Converting kVA to Amps might seem simple, but errors are common. Avoiding these mistakes ensures accurate electrical calculations.
Incorrect Variable Identification
One common mistake is confusing kVA with kW or V. These variables are different. kVA stands for kilovolt-amps, a unit of apparent power. kW is kilowatts, a unit of real power. V is volts, a measure of electrical potential. Mixing these variables leads to incorrect calculations.
Identify each variable correctly before converting. Here’s a quick reference:
| Variable | Meaning |
|---|---|
| kVA | Kilovolt-Amperes (Apparent Power) |
| kW | Kilowatts (Real Power) |
| V | Volts (Electrical Potential) |
Misapplication Of Formula
Another common error is using the wrong formula for conversion. The correct formula depends on the phase of the system. For single-phase systems:
A = (kVA 1000) / V
For three-phase systems:
A = (kVA 1000) / (√3 V)
Using the wrong formula leads to inaccurate results. Ensure you know the system type before converting.
Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Identify the system phase (single or three-phase).
- Choose the correct formula.
- Insert the correct values for kVA and V.
- Calculate the Amps.
Avoiding these mistakes ensures precise conversions and safe electrical operations.
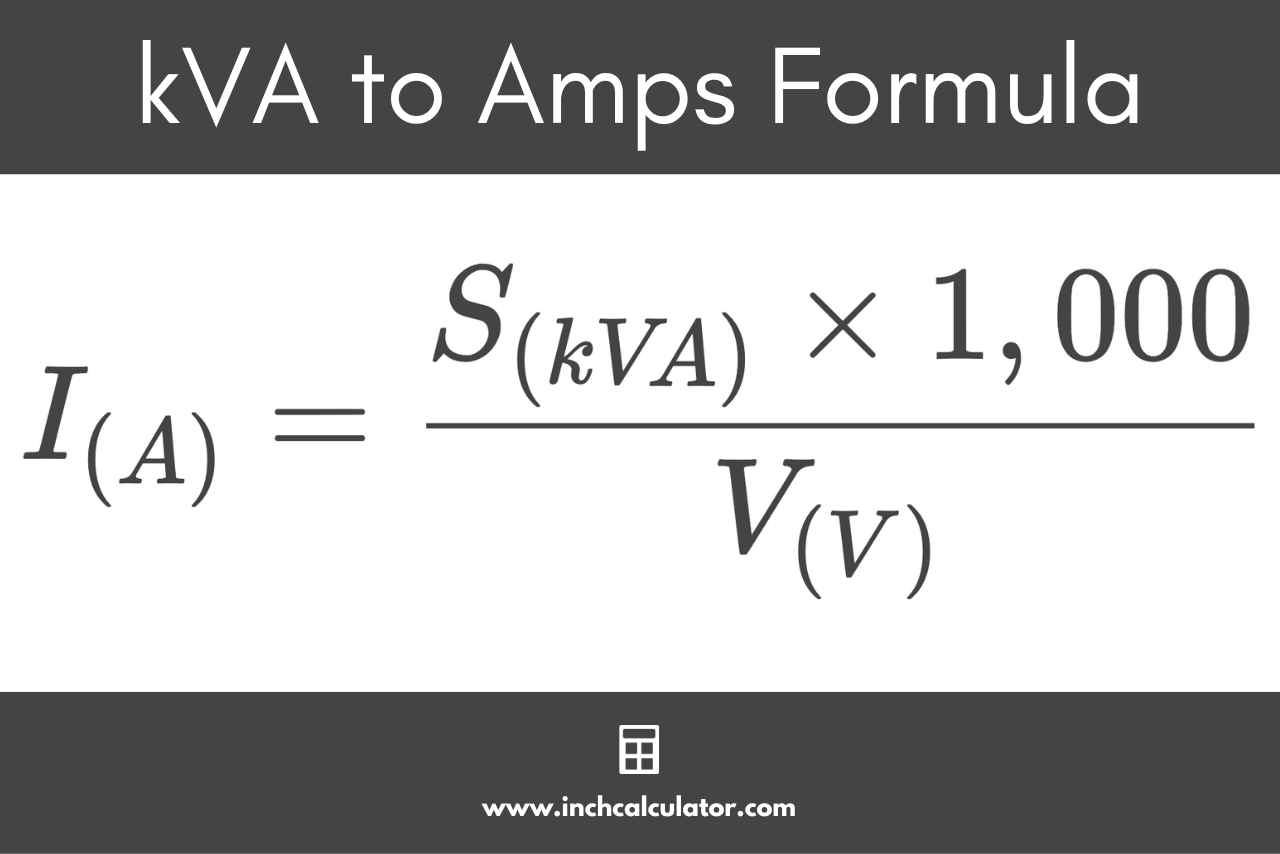
Credit: www.inchcalculator.com
Applications In Real-world Scenarios
Understanding the conversion of KVA into Amps is crucial in various real-world scenarios. This knowledge helps ensure electrical systems operate efficiently. Let’s explore its applications in industrial and residential settings.
Industrial Settings
In industrial settings, machinery often requires precise power calculations. Converting KVA into Amps ensures equipment operates safely.
- Large motors and transformers need accurate power assessments.
- Factories use this conversion to manage electrical loads.
- It helps prevent overloading and potential equipment damage.
Example calculation:
For a 3-phase system:
KVA = 100
Voltage = 400V
Amps = (KVA 1000) / (Voltage √3)
Amps = (100 1000) / (400 1.732)
Amps ≈ 144.34Residential Use
In homes, converting KVA into Amps helps manage appliances and circuits. This ensures electrical safety and efficiency.
- Homeowners use this for backup generators.
- It helps in setting up home electrical systems.
- Electricians use it for planning and troubleshooting.
Example calculation:
For a single-phase system:
KVA = 5
Voltage = 230V
Amps = (KVA 1000) / Voltage
Amps = (5 1000) / 230
Amps ≈ 21.74Frequently Asked Questions
What Is 1 Kva In Amps?
1 kVA equals 1,000 volt-amps. To convert kVA to amps, divide by the voltage (in volts). For example, with 240 volts, 1 kVA equals 4. 17 amps.
How To Convert Kva To Amps?
To convert kVA to amps, use the formula: Amps = kVA × 1000 / Voltage. Ensure you know the voltage type.
How Many Amps Is 30 Kva?
30 kVA equals 125 amps at 240 volts. Divide kVA by voltage and multiply by 1000 to get amps.
How Many Amps Is 10 Kva?
10 kVA equals 41. 67 amps at 240 volts, or 83. 33 amps at 120 volts. Divide 10,000 by voltage to get amps.
Conclusion
Understanding kVA to Amps conversion is crucial for electrical projects. It ensures safety and efficiency. This knowledge helps in selecting the right equipment and avoiding overloads. Stay informed and make smart decisions to keep your electrical systems running smoothly. Your expertise in this area can save time, money, and prevent potential hazards.