Ground and neutral are both electrical paths returning current to its source; ground is for safety, neutral for circuit completion. These wires serve distinct but vital roles in electrical systems.
Understanding the difference between ground and neutral wires is crucial for safe electrical installations. The neutral wire acts as the return pathway for the electrical current supplied through the live wire. It’s a central part of the electrical circuit, allowing the successful completion of the electrical loop.
On the other hand, the ground wire, also known as the earth wire, doesn’t carry current under normal operations. Its primary purpose is to provide a path for electrical current to dissipate safely in case of a fault, such as a short circuit. This helps to protect both the electrical system and users from potential electric shock or fires. Recognizing the functionality of both ground and neutral wires is fundamental in any electrical system, safeguarding both efficiency and safety.
Ground And Neutral Basics
Welcome to our exploration of the electrical world where we simplify complex concepts. Today, we unravel the mysteries of ground and neutral wires in electrical systems. Think of them as the unsung heroes keeping our appliances safe and our power flowing smoothly. Let’s dive into the basics of ground and neutral wires to understand their critical roles.
The Role Of Ground In Electrical Systems
The ground wire acts as a safety net. It is the backup path that provides a safe route for electrical current to travel to the earth in case of a fault. This prevents electric shocks and protects the system. Here’s what you need to know about grounding:
- Connected to the earth — offers safety during excess current events.
- Second path — protects by providing an alternate route for electricity.
- Reduces shock risk — keeps electrical systems stable and people safe.
The Function Of Neutral In Power Distribution
Neutral wires complete the circuit in a power distribution system. They ensure currents return safely after powering our devices. The neutral wire is the return path for electric current back to the source. Key points about neutrals include:
- Balances the electrical system — allows for efficient current flow.
- Carries current under normal conditions— returns power to the source.
- Zero potential energy — references to the earth for safety and stability.
These two wires, ground and neutral, may seem similar. But they have distinct functions that enhance safety and functionality in electrical systems. Remember, never use ground and neutral wires interchangeably. Doing so can lead to hazardous situations and the potential for electrical hazards. Understanding their roles is essential for anyone dealing with electricity, no matter how simple or complex the task.
Historical Development
The journey behind the electrical systems we rely on today is rich with innovation and an unwavering focus on safety. Understanding the distinction between ground and neutral wires helps grasp the advancements made in electrical safety. Let’s dive into the historical development of these crucial elements of modern electricity.
The Evolution Of Electrical Wiring Standards
The story of electrical wiring is one of constant improvement. It began in the late 19th century when electricity started lighting up our cities. At first, electrical systems were erratic and dangerous. Wiring standards did not exist, which led to frequent accidents and fires.
By the early 20th century, the need for safer electrical systems became clear. This led to the creation of National Electrical Code (NEC), which set the first safety standards for wiring. These standards have evolved, driven by technological advances and a deeper understanding of electrical safety.
- Introduction of insulated wiring
- Requirement of grounded circuits
- Standards for neutral wires
Significant Milestones In Safety Regulations
The timeline of safety regulations is marked by key milestones that have revolutionized electrical safety.
| Year | Milestone | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 1897 | First edition of NEC | Introduced basic safety guidelines |
| 1923 | Polarized receptacles | Reduced shock risk |
| 1962 | Ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) | Prevented electrical shocks near water |
| 1981 | Ground and neutral bonding requirement | Enhanced overall system safety |
These milestones have been crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring electrical systems are safe for public and private use. Innovations like the GFCI and continuous enhancements of the NEC keep pushing the boundaries of electrical safety.
Distinctions Between Ground And Neutral
In the world of electricity, both ground and neutral ensure safety and functionality. Yet, they serve distinct roles and characteristics. Understanding the differences between these two can ensure proper wiring and enhance electrical safety. With this, let’s delve into what separates ground from neutral.
Key Differences In Purpose And Function
- Ground: A safety path for electricity during a fault
- Neutral: Returns current back to the power source
A ground wire is a backup path for electricity. It only carries current if there is a problem. The neutral wire carries current back to the source during normal operations.
Electrical Potential And Current Carrying Characteristics
| Aspect | Ground | Neutral |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Potential | Should not have electrical potential | Carries low potential |
| Current Carrying | Carries current only during a fault | Carries current during normal operation |
The ground wire is designed to be at zero electrical potential. So, it should not carry voltage under normal circumstances. The neutral wire normally carries the current back to the power source at a low potential.
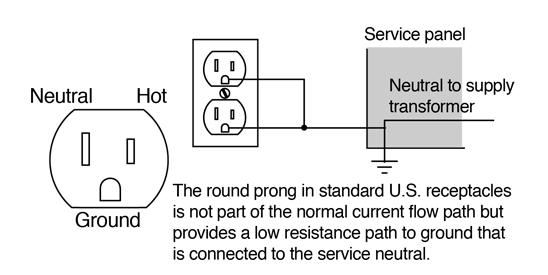
Credit: hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu
Safety Implications
Understanding the roles of ground and neutral wires is key to preventing electrical hazards. These wires serve different safety functions in an electrical system. It is crucial for the safety of any household or building. Let’s explore how both contribute to a safer environment.
Preventing Electric Shocks
Ground wires protect people from electric shocks. They provide a path for electrical current if a fault occurs. This helps to avoid the risk of the current passing through a person.
- Ground connections divert current away from appliances to the earth.
- They prevent the build-up of voltages that could lead to shock.
- Electrical systems must have proper earth bonding. This ensures user safety.
Mitigating The Risk Of Electrical Fires
Neutral wires complete the electrical circuit and help prevent fires. They carry current back to the power source.
- Neutral wires should connect securely to the main panel.
- Loose connections can create sparks.
- These sparks can ignite surrounding materials.
| Component | Function | Safety Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Ground Wire | Diverts fault current | Prevents shocks |
| Neutral Wire | Carries current back | Reduces fire risk |
Maintaining an electrical system is vital. Homes should undergo regular electrical inspections. This ensures safety features are working correctly.
Electrical System Design
The design of an electrical system is key to safe and efficient operation. Ground and Neutral are two terms often discussed together but serve different purposes. Understanding their roles and configurations in home wiring is crucial. Knowledge of critical considerations in industrial design is equally important. Both ensure that systems function correctly and protect against electrical hazards.
Ground And Neutral Configurations In Home Wiring
In home electrical systems, ground and neutral wires play vital roles. The neutral wire acts as the return path for current to complete the circuit. The ground wire provides an additional path for electric current to return safely to the ground in case of a fault. These wires must be configured correctly in your home.
- The neutral wire is usually white or grey.
- The ground wire is either green or bare without insulation.
- Neutral and ground wires connect separately to the main panel.
- Electrical outlets have dedicated terminals for ground and neutral.
Critical Considerations In Industrial Electrical Design
In industrial settings, electrical system design takes on greater complexity. Systems must handle higher loads and harsher environments. Safety, reliability, and compliance with codes are essential. Here are some critical considerations:
- Designs must include fault detection systems to prevent accidents.
- Ground and neutral paths should be thoroughly separated to avoid potential hazards.
- Regular maintenance checks are crucial for operational integrity.
- Systems require scalability and flexibility to adapt to changing demands.
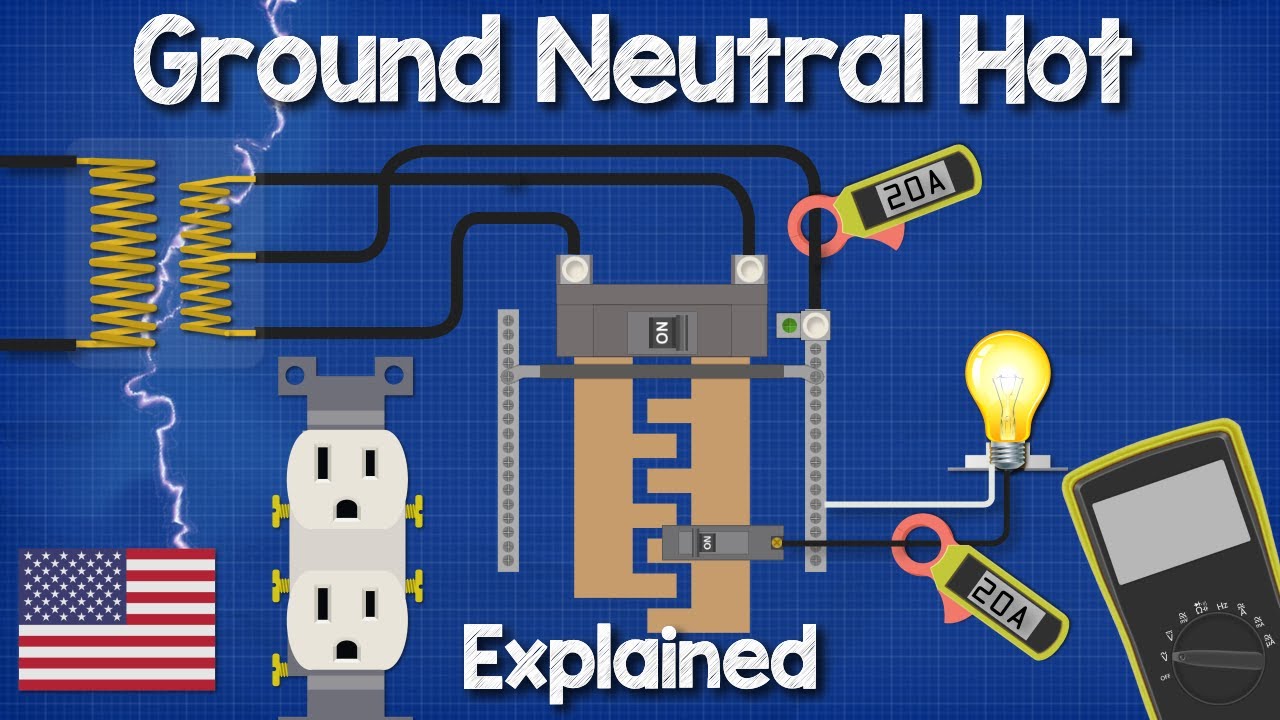
Credit: www.youtube.com
Understanding Ground Faults
A ground fault is a type of electrical mishap. It happens when electricity takes a path it shouldn’t. This can occur if there’s a break in wiring or devices are damaged. Understanding this can keep us safe. It’s like teaching a river to flow where it should.
Identifying and Diagnosing Ground FaultsIdentifying And Diagnosing Ground Faults
Spotting a ground fault means looking for signs carefully. Think of it as electrical detective work. We can notice things like:
- Telltale Trips: Circuit breakers tripping often.
- Shock Sensations: Mild shocks from appliances or tools.
- Buzzing Sounds: Unusual noises from electrical systems.
Diagnosing these faults needs special tools. Electricians use a clamp meter to see if the fault’s live. They test circuits to find the escape path for electricity.
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) in ActionGround Fault Circuit Interrupters (gfcis) In Action
A GFCI is a superhero device for our homes and offices. It watches over the flow of electricity. When it senses a ground fault, it acts fast. It cuts off power in a fraction of a second. This helps prevent fires and shocks.
We can find GFCIs in places near water like kitchens and bathrooms. They are in the form of outlets or breaker switches. They are tested regularly to ensure they work right. Pushing the “test” button is the quick way to check them.
| Action | Result |
|---|---|
| Press “Test” | GFCI should power off. |
| Press “Reset” | GFCI should power on. |
National And International Standards
Understanding the role of ground and neutral connections is critical for electrical safety and functionality in any power system. These connections adhere to strict standards that vary across regions. Here we delve into national and international standards governing these essential components of electrical systems.
The Nec And Iec On Ground And Neutral
The National Electrical Code (NEC) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) set the benchmark for safety in electrical installations. The NEC is a North American standard, while the IEC governs international practices. Both address ground and neutral connections to ensure user safety and prevent electrical faults.
- The NEC defines ground as an auxiliary path for electrical current to return to the source during a fault.
- Neutral is described as a normal conductor that carries current back to the source during regular operation.
Furthermore, these standards make a clear distinction. The ground must not carry current under normal operating conditions. On the other hand, a neutral typically does. This distinction is crucial for the proper functioning of electrical systems. The NEC and IEC detail how to properly install and maintain these components.
Harmonization Of Safety Standards Across Borders
In a globalized world, harmonizing safety standards is paramount. Electrical products and professionals cross borders more than ever. Similar standards for ground and neutral ensure higher safety and easier compliance.
| Region | Applicable Ground/Neutral Standards |
|---|---|
| North America | NEC, ANSI |
| Europe | IEC, EN |
| Asia | Various National Standards, IEC recommendations |
International partnerships among standards organizations strive to align safety policies. This makes global trade of electrical equipment more manageable. It helps professionals around the world to adhere to commonly accepted practices.
Safety is the primary concern. Ground and neutral wires must meet these standards. This ensures that appliances and equipment operate safely. Users across the globe can trust in the reliability and safety of their electrical systems.
Testing And Maintenance
Your home’s electrical system relies on a robust ground and neutral configuration for safety and efficiency. Regular testing and maintenance of these essential wiring components can prevent electrical hazards. Ensure these systems are functioning properly with a thoughtful approach to inspection and upkeep.
Procedures For Checking Ground And Neutral Integrity
Maintaining the integrity of ground and neutral wires is critical. Use the following steps to assess their condition:
- Turn off the power supply to the circuit you’re testing.
- Locate the ground and neutral connections in your electrical panel.
- Use a multimeter set to the resistance setting, and check for continuity between the ground and the neutral bar.
- A reading of zero or close to zero indicates a good connection.
- If the reading is high, this suggests a possible break or poor connection needing attention.
- Inspect visually for signs of corrosion or damage on both the neutral and ground systems.
- Ensure all connections are secure.
These steps help identify potential issues, allowing for timely repairs.
The Importance Of Regular Electrical Inspections
Regular inspections of your electrical system serve as proactive measures to prevent electrical failure and ensure safety. Here’s why they are important:
- Identify potential hazards before they cause harm.
- Maintain effective and efficient electrical system operation.
- Extend the lifespan of your electrical components by addressing wear and tear.
- Compliance with local electrical codes and standards.
- Peace of mind knowing your home is safe from electrical risks.
Engage a licensed electrician for a thorough inspection annually. Between professional inspections, homeowner vigilance with the described testing procedures also plays a vital role.
Real-world Incidents And Case Studies
Understanding Ground Vs Neutral is vital in the world of electricity. Let’s explore real incidents and case studies.
Learning From Past Electrical Mishaps
Throughout history, electrical mishaps have served as tough lessons. We learn and improve safety standards through these events.
- Case Study: Overloaded Circuits – A home faced a fire due to overloaded circuits. It caused neutral confusion and a deadly fault.
- Mishap: Improper Grounding – A factory experienced equipment failure. The ground and neutral wires were wrongly connected.
Innovations Prompted By Historical Accidents
Historical accidents have prompted breakthroughs in electrical safety. This leads to safer and more intuitive systems.
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) – Invented to prevent electrocution by detecting ground faults.
- Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs) – Created to protect against fires caused by arcing faults.
These innovations arose from the ashes of electrical mishaps.

Credit: www.linkedin.com
Future Of Electrical Safety
The Future of Electrical Safety is a vibrant, evolving landscape. Innovations are continuously shaping the way electricity is managed within homes and industries. Understanding the relationship between ground and neutral wires is crucial to leverage these advancements for enhanced safety. Let’s explore how emerging technologies are set to redefine electrical safety.
Advancements In Circuit Protection Technologies
Circuit protection has come a long way. Today’s technologies not only safeguard wiring but also help prevent electric shocks. One significant development is the Arc-Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs). These devices detect dangerous arc patterns and cut the power before a fire can start.
Another notable innovation is the Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI). GFCIs promptly switch off power when they sense current flowing along an unintended path. This can occur if a person becomes part of the circuit, preventing harmful shocks.
Emerging technologies focus on enhancing these systems. They integrate sensors and connectivity for real-time monitoring and issue detection. Sophisticated diagnostics pinpoint exact locations of faults, making repairs more efficient.
Trends In Smart Home Electrical Systems
Smart homes are altering electrical safety dynamics. These systems harness the power of the Internet of Things (IoT) for greater control and efficiency. We now have smart circuit breakers controlled via mobile apps, offering remote troubleshooting and improved electrical flow management.
Another trend is energy monitoring in real-time. Devices can analyze electricity usage and adjust the flow to reduce hazards and conserve power. Plus, smart outlets and switches include built-in GFCIs for enhanced safety.
- User-friendly interfaces for monitoring power usage
- Automatic shutdown during overload or fault conditions
- Customizable alerts for potential electrical issues
These innovations promise to keep homes and their inhabitants safer from electrical mishaps. Integrating ground and neutral systems with smart technologies paves the way for not just safe, but incredibly intelligent electrical infrastructures.
Frequently Asked Questions For Ground Vs Neutral
What Is The Difference Between Ground And Neutral?
Ground and neutral are different paths in electrical systems. The ground offers protection by redirecting excess electricity, while neutral functions as a return path for the current.
Why Is Grounding Necessary In Electrical Systems?
Grounding is essential for safety. It prevents electrical shock by redirecting excess electricity into the earth, vastly reducing the risk of injury or fire.
Can Neutral And Ground Wires Be Connected?
Neutral and ground wires should not be connected inside electrical outlets or panels, except at the main service panel, as it can lead to potential hazards.
How Do Ground And Neutral Wires Improve Safety?
Both wires improve safety by managing electricity flow. The neutral returns current to the power source, while the ground disperses unwanted electricity, preventing shocks and fires.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinct roles of ground and neutral is crucial for electrical safety and efficiency. Both carry out essential, yet separate functions in any electrical system. By respecting these differences, we not only ensure our appliances operate properly but also safeguard our homes from potential hazards.
Always consult a professional for electrical concerns for optimal safety. Keep the ground and neutral in their respective places—your electronics will thank you.