A distribution line carries electricity from substations to consumers. These lines are integral to the electrical grid’s infrastructure.
Understanding the function of distribution lines is crucial for grasping how power reaches our homes and businesses. Typically mounted on poles or laid underground, these lines form extensive networks that traverse cities, suburbs, and rural areas. They operate at lower voltages than transmission lines, which are responsible for moving electricity over long distances.
The distribution system includes transformers that step down voltage levels to make the power safe for domestic and commercial use. Safe, efficient, and reliable distribution lines are essential for a steady supply of electricity, which powers our daily lives and drives the economy. Their maintenance and upgrades are critical for meeting growing energy demands and integrating renewable energy sources into the power grid.

Credit: www.ysgsolar.com
Importance Of Distribution Line
The Importance of Distribution Line in a power system network cannot be overstated. These lines serve as the critical link between the electricity generated at power stations and the end-users. They are the final stage in the delivery of electricity to homes and businesses. A robust and well-maintained distribution line network ensures a steady flow of power, minimal interruptions, and efficient energy use. Let’s delve into why these lines are so crucial to our daily lives.
Reliability Of Power Supply
Reliable electricity is essential for modern life. Distribution lines play a key role in providing this. They must withstand various challenges such as bad weather, equipment failures, and surges in demand. Strong distribution lines mean fewer power cuts and more consistent electricity. This reliability supports critical services like hospitals and emergency services. It also helps everyday activities like cooking, studying, and entertainment.
Efficiency In Power Distribution
Efficiency means doing more with less. In power distribution, it means delivering electricity without losing much energy. Good distribution lines reduce energy loss. This is important for saving resources and keeping costs down. Efficient lines also lower the environmental impact of power delivery. This is because they help in using less fuel to generate electricity.
- Reduced energy losses lead to lower operational costs.
- Optimized voltage levels ensure appliances work correctly.
- Improved grid stability prevents outages and voltage dips.

Credit: www.ysgsolar.com
Components Of Distribution Line
Distribution lines are crucial for delivering electricity. They have several key components. Each part plays a vital role in ensuring power reaches our homes and businesses safely and efficiently.
Power Lines
Power lines are the main carriers of electricity. They spread across cities and countryside to deliver power. Made of conductive materials, they handle high voltages over long distances. Here are important facts about power lines:
- Copper or aluminum wires are common.
- They can be overhead or underground.
- Safety is crucial, so they are placed high or buried deep.
Transformers
Transformers adjust the voltage of electricity to usable levels. This is essential for safe home and business use. Key points about transformers include:
| Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Step-up | Increases voltage for transmission |
| Step-down | Reduces voltage for safety |
Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers protect our electrical devices. They stop too much electricity from causing damage. Here’s how they help:
- Automatically shut off electricity during faults.
- Prevent fires and protect equipment.
- Easy to reset and continue use.
Each component of a distribution line ensures that electrical systems run smoothly and safely. Understanding these parts helps us appreciate the complexity and importance of our electrical infrastructure.
Types Of Distribution Lines
Electricity travels a long path before it powers our homes. This journey happens through distribution lines. These lines are the final stage in the delivery of electricity. They come in different types to suit various needs and environments. Let’s explore the different kinds of distribution lines that bring power to our lives.
Overhead Lines
Overhead lines are the most common type. You can see them in the sky on tall poles. They carry electricity through wires high above the ground. Here are some key points about overhead lines:
- Visible: Easy to spot against the sky.
- Air cooling: The air naturally cools the wires.
- Space: They need space away from trees and buildings.
- Repair: Easy to fix because they are easy to reach.
Underground Lines
Underground lines are hidden from view. They run below the earth’s surface. These lines are used in places where overhead lines are not suitable. Their features include:
- Protected: Safe from storms and falling trees.
- Discrete: They do not change the look of an area.
- Maintenance: Harder to reach if there’s a problem.
- Cost: More expensive to install than overhead lines.
Hybrid Lines
Hybrid lines are a mix of both overhead and underground lines. They combine the best of both worlds. Hybrid lines are used in special cases:
| Where Used | Why Used |
|---|---|
| Urban Areas | Space is limited for poles. |
| Natural Reserves | Protects the view and wildlife. |
| Coastal Regions | Prevents salt damage to wires. |
Credit: lge-ku.com
Challenges Faced In Distribution Lines
The vitality of our day-to-day lives hinges on the seamless operation of distribution lines. These lines crisscross cities and countryside alike, powering homes, businesses, and essential services. Yet, maintaining this vast network is no small feat. Operators face a myriad of challenges that can affect performance and reliability.
Aging Infrastructure
As time marches on, so does the wear on our electrical distribution systems. Many components are well past their prime. This can lead to increased faults, outages, and safety hazards. Upgrading these systems is a massive undertaking, both in terms of cost and logistics.
- Increased maintenance costs
- Higher failure rates
- Safety concerns
Weather doesn’t play by the rules, and distribution lines often bear the brunt of its fury. From hurricanes to ice storms, these events can wreak havoc, causing widespread damage and long recovery times.
| Weather Event | Impact on Distribution Lines |
|---|---|
| High Winds | Downed lines, power outages |
| Ice/Snow | Line breaks, equipment strain |
| Flooding | Submerged equipment, access issues |
Technological Advancements In Distribution Lines
The electric grid is evolving rapidly. New technologies are changing how we distribute electricity. These advancements make the grid more reliable, efficient, and greener. Let’s explore how modern tech is reshaping distribution lines.
Smart Grid Technology
Smart Grids are the future. They use digital communication to detect and react to local changes in usage. This means:
- Better balance between electricity supply and demand
- Reduced outages and faster repair times
- Integration of renewable energy sources
Smart meters allow real-time energy tracking. Consumers can see their usage and save money. Utilities can manage the grid more effectively.
Distributed Energy Resources
Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) are small-scale electricity sources. They are close to where the energy is used. DERs include:
| Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Solar Panels | Homes, businesses |
| Wind Turbines | Small farms, community projects |
| Batteries | Energy storage systems |
DERs help reduce the strain on the grid. They provide clean, local power. This makes the grid more flexible and less dependent on central power plants.
Future Trends In Distribution Lines
The electric grid is evolving rapidly. Advancements in technology shape the future of distribution lines. Understanding these changes helps us prepare for a more efficient and reliable energy future.
Grid Modernization
Smart grids are the future. They make power distribution more reliable. Smart grids use technology to detect and react to local changes in usage. This leads to a more efficient power system. With smart meters and advanced sensors, grid modernization ensures better energy management.
- Real-time monitoring: Quick identification of issues for faster response.
- Automated controls: Self-healing from power disturbances.
- Energy efficiency: Reduced peak demand, which lowers electricity rates.
Electrification Of Transportation
Electric vehicles (EVs) are changing our roads. EVs need power from distribution lines. The rise of EVs creates new demands on the grid. Charging stations are becoming more common.
| Impact on Distribution Lines | Response Required |
|---|---|
| Increased Load | Grid upgrades for higher capacity |
| Peak Demand | Smart charging strategies |
Utilities must adapt. They need to support the growing number of EVs. This includes upgrading transformers and installing new lines where needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
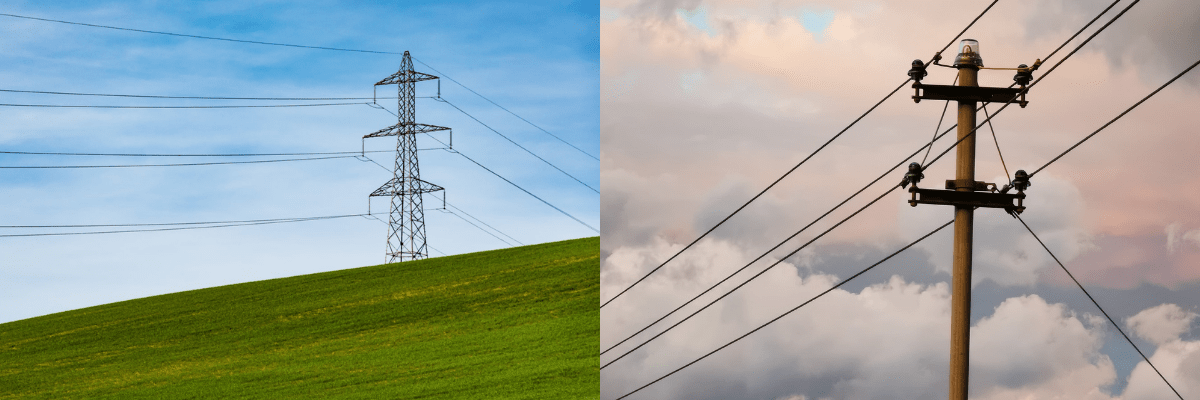
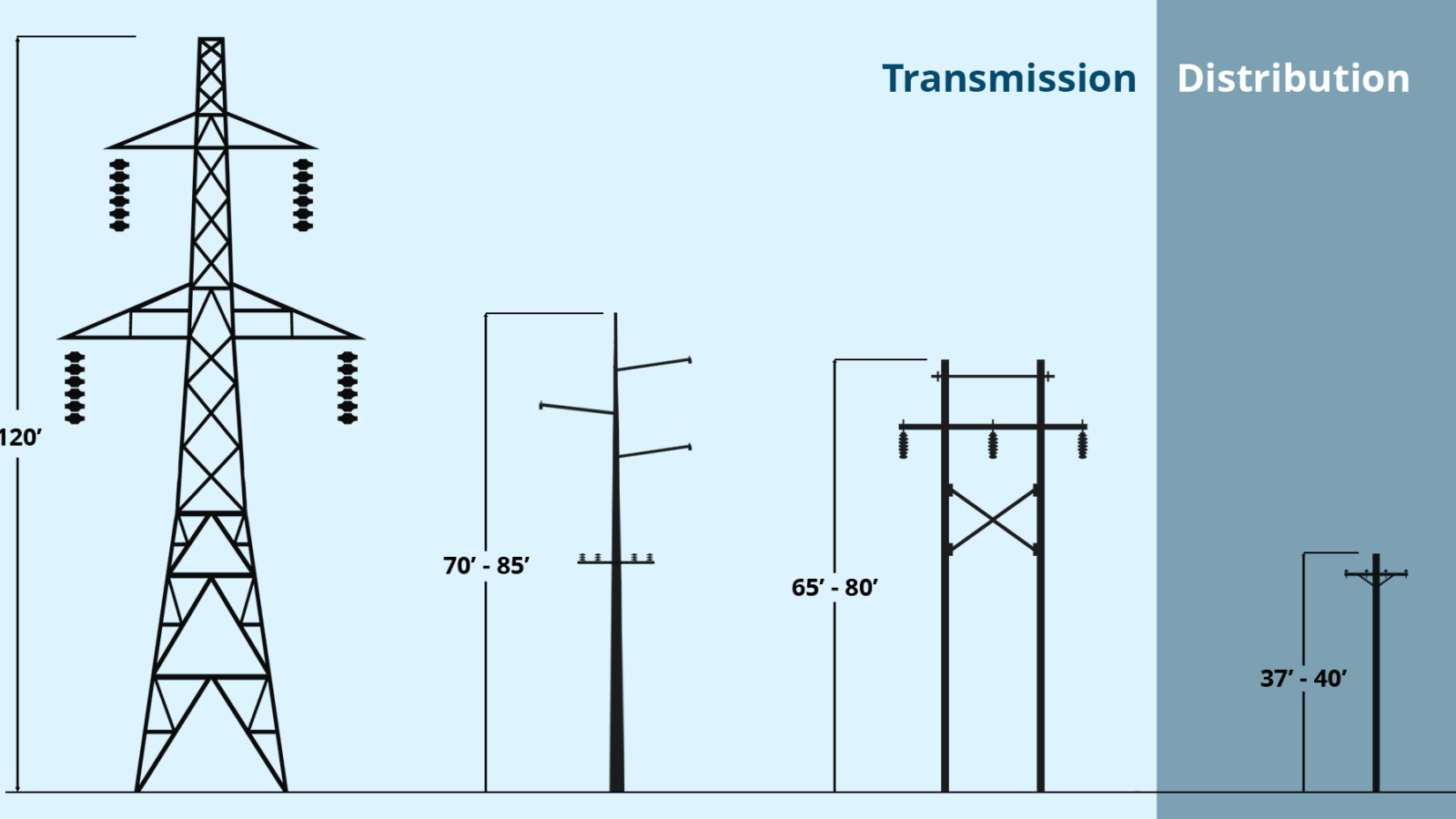
What Is The Difference Between The Transmission Line And Distribution Line?
Transmission lines carry high voltage electricity over long distances, typically from power plants to substations. Distribution lines, in contrast, deliver lower voltage power from substations to consumers, such as homes and businesses. This structure enhances efficiency and safety in power delivery.
How Many Volts Are In A Distribution Line?
Distribution lines typically carry voltages ranging from 4,000 to 35,000 volts (4 to 35 kilovolts).
What Is The Primary Distribution Line?
The primary distribution line carries electricity from substations to transformers before reaching local users.
How Do You Identify A Transmission Line And A Distribution Line?
To identify a transmission line versus a distribution line, note their appearance and function. Transmission lines have taller towers and thicker cables, carrying high voltage power over long distances. Distribution lines, on the other hand, use shorter poles and thinner wires to deliver electricity locally at lower voltages.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of distribution lines is essential for efficient energy delivery. This post highlighted their significance, challenges, and advancements. Embrace these insights to optimize your network’s performance. Remember, the power of a strong distribution system sparks more than just homes—it ignites progress.

