A Class A Lineman installs, maintains, and repairs high-voltage power lines. They ensure the safe and efficient transmission of electricity.
A Class A Lineman plays a vital role in the electrical industry. They work with high-voltage systems to ensure reliable power distribution. Their job involves climbing poles, working in challenging conditions, and handling complex equipment. These linemen must follow strict safety protocols to prevent accidents.
They also need to respond quickly to power outages and emergencies. Training and experience are crucial for this demanding job. Proper certification and continuous education help them stay updated with the latest technologies and safety standards. A Class A Lineman’s expertise ensures that communities have uninterrupted access to electricity, making their role indispensable.
Introduction To Class A Lineman
A Class A Lineman is vital in the electrical industry. They ensure that power lines are installed and maintained. Their work keeps homes and businesses connected to power.
Role And Responsibilities
A Class A Lineman handles many tasks. These tasks include:
- Installing new power lines
- Maintaining existing power lines
- Repairing damaged power lines
- Ensuring safety procedures
- Working in various weather conditions
They also use specialized tools and equipment. They climb poles and work on high voltage lines. Safety is their top priority.
Importance In The Industry
Class A Linemen are essential in the electrical industry. They ensure reliable power supply to homes and businesses. Without them, power outages would be more common.
Their work supports the daily operations of many industries. Schools, hospitals, and factories rely on their expertise. They help keep the community safe and functioning.
Training and experience make them experts in their field. They undergo rigorous training to handle their tasks safely. Their skills are in high demand across the country.
Credit: energized.edison.com
Training And Certification
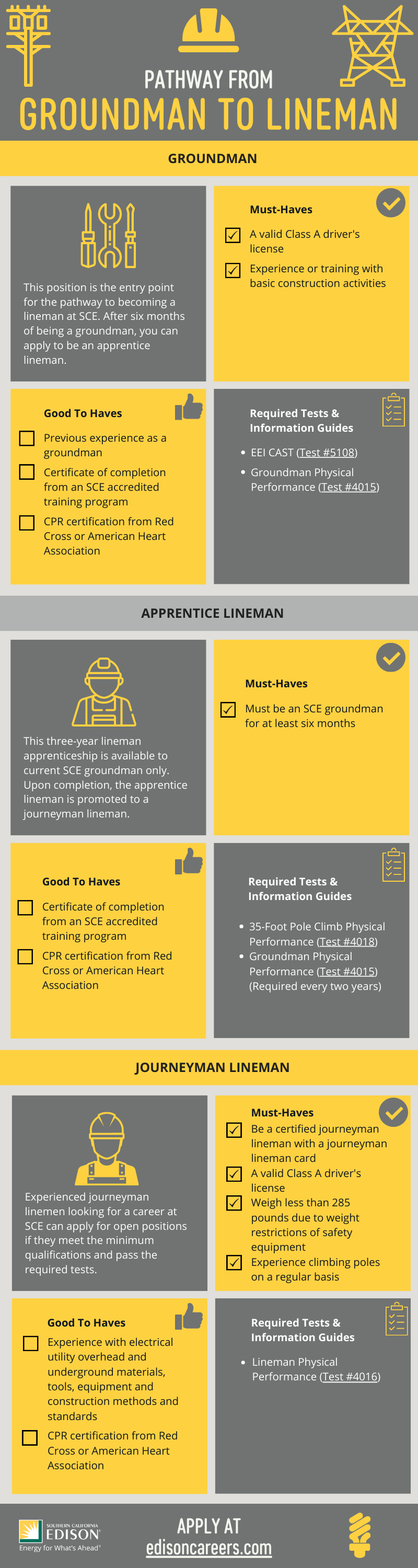
Becoming a Class A Lineman is a rewarding career. It involves rigorous training and certification. This section will cover the essential educational requirements and the certification process.
Educational Requirements
To become a Class A Lineman, a high school diploma is essential. Proficiency in math and science helps. Knowledge in electrical systems and physical fitness is crucial.
| Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
| High School Diploma | Basic educational qualification |
| Math and Science | Important for understanding electrical systems |
| Physical Fitness | Necessary for the demanding work environment |
Certification Process
The certification process involves several steps. Completing an apprenticeship program is the first step. This program typically lasts four years.
- Complete Apprenticeship: Four years of on-the-job training.
- Pass Exams: Written and practical tests are mandatory.
- Obtain Certification: Certification from a recognized body like the Department of Labor.
During the apprenticeship, trainees gain hands-on experience. They learn under the guidance of skilled linemen. This program includes classroom instruction and fieldwork.
After completing the apprenticeship, passing the exams is crucial. These exams test both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Successful candidates receive certification, marking them as qualified Class A Linemen.
This certification is recognized nationwide. It ensures linemen have the necessary skills and knowledge. Continuous education and training are required to maintain certification.
Essential Skills
Being a Class A Lineman demands a unique set of skills. These skills ensure safety and efficiency on the job. This section will highlight the essential skills a Class A Lineman must possess.
Technical Proficiency
A Class A Lineman must have strong technical proficiency. They need to understand electrical systems and components. Knowledge of wiring diagrams and blueprints is crucial. They should also know how to use various tools and equipment.
Here are some key technical skills:
- Reading and interpreting wiring diagrams
- Operating specialized tools
- Understanding electrical codes and standards
- Performing installations and repairs
| Skill | Description |
|---|---|
| Blueprint Reading | Ability to read and understand technical diagrams. |
| Tool Operation | Proficiency with electrical tools and equipment. |
| Safety Standards | Knowledge of industry safety protocols. |
Problem-solving Abilities
Problem-solving is a critical skill for a Class A Lineman. They often encounter unexpected issues. Quick thinking and effective solutions are necessary. They must stay calm under pressure.
Important aspects of problem-solving:
- Identifying the problem
- Analyzing possible causes
- Formulating a plan of action
- Implementing the solution
These steps ensure that issues are resolved efficiently. Having problem-solving abilities makes the lineman’s job smoother and safer.
Safety Protocols
Ensuring the safety of Class A Linemen is crucial. Safety protocols help prevent accidents and injuries. These protocols cover a wide range of practices. The most important include personal protective equipment and emergency procedures. Let’s break them down further.
Personal Protective Equipment
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is essential for every lineman. PPE protects linemen from electrical hazards and physical injuries. Here are some critical PPE items:
- Hard Hats: Protect the head from falling objects.
- Insulated Gloves: Prevent electric shocks.
- Safety Glasses: Shield the eyes from debris.
- Flame-Resistant Clothing: Reduce burn injuries.
- Steel-Toe Boots: Protect feet from heavy objects.
Each piece of PPE must be in excellent condition. Regular checks and maintenance are necessary. Linemen should also be trained on proper usage.
Emergency Procedures
Emergencies can happen anytime. Having clear emergency procedures is vital. These procedures include steps to take during an accident or hazardous situation.
- Assess the Situation: Quickly evaluate the danger level.
- Call for Help: Contact emergency services immediately.
- First Aid: Administer first aid if trained and safe to do.
- Evacuation: Evacuate the area if the danger persists.
- Report Incident: Document and report the incident for further review.
Training on these procedures is essential. Regular drills ensure everyone knows their role in an emergency. Proper training can save lives.
| Emergency Contact | Phone Number |
|---|---|
| Fire Department | 123-456-7890 |
| Medical Emergency | 098-765-4321 |
| Company Safety Officer | 555-555-5555 |
By following these safety protocols, Class A Linemen can work more safely. Adherence to these practices ensures a safer work environment for all.
High Voltage Work
Class A Linemen deal with high voltage work. This job requires great skill and safety. Linemen ensure the power stays on. They work on electrical lines and equipment. Safety is their top priority.
Handling High Voltage Equipment
Linemen handle high voltage equipment daily. They use special tools to stay safe. These tools include insulated gloves and hot sticks. Linemen must check their tools before use.
Proper training is key for handling this equipment. Linemen learn how to use equipment safely. They also learn how to handle emergencies. This training keeps them safe on the job.
Live Line Work Techniques
Live line work means working on live electrical lines. Linemen use special techniques for this work. These techniques prevent electric shocks. One technique is the hot stick method.
Another technique is the barehand method. Linemen wear special suits for this method. These suits protect them from high voltage. Proper technique is crucial for safety.

Credit: richmondcc.edu
Tools And Equipment
A Class A Lineman needs specialized tools and equipment. These tools ensure safety and efficiency. From basic hand tools to advanced technology, each tool serves a vital purpose.
Standard Tools
Every Class A Lineman carries a set of standard tools. These tools include:
- Insulated Pliers: Essential for gripping and cutting wires safely.
- Wire Strippers: Used for removing insulation from electrical wires.
- Wrenches: Necessary for tightening and loosening nuts and bolts.
- Voltage Tester: Ensures circuits are de-energized before work begins.
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Insulated Pliers | Gripping and cutting wires |
| Wire Strippers | Removing insulation from wires |
| Wrenches | Tightening and loosening nuts |
| Voltage Tester | Ensuring circuits are de-energized |
Advanced Technology
Advanced technology tools make the lineman’s job easier and safer. These tools include:
- Smart Meters: Measure electrical usage accurately.
- Thermal Imaging Cameras: Detect hot spots in electrical systems.
- Drones: Inspect hard-to-reach areas from a safe distance.
- Augmented Reality Glasses: Provide real-time data and instructions.
These tools help linemen perform tasks efficiently. They also enhance safety by providing crucial data.
Challenges In The Field
The job of a Class A Lineman is highly demanding. Linemen face numerous challenges daily. These can range from harsh weather conditions to intense physical demands. Here, we explore the key challenges that linemen encounter in their line of work.
Weather Conditions
Class A Linemen work outdoors, making them vulnerable to harsh weather. Extreme weather conditions can pose serious risks. Rain, snow, and sleet can make surfaces slippery. High winds can destabilize equipment and personnel. Lightning poses a significant danger to linemen working on elevated structures.
During summer, heat exhaustion and dehydration are common issues. The sun’s rays can be relentless, making the job even harder. Winter brings its own set of challenges. Freezing temperatures can cause numbness and reduce mobility. It is crucial to wear appropriate gear for protection.
Physical Demands
Being a Class A Lineman requires a high level of physical fitness. The job involves lifting heavy equipment and tools. Linemen must climb tall structures and work at great heights. This demands not only strength but also stamina and balance.
Linemen often work in awkward positions for extended periods. This can lead to muscle strain and fatigue. Back injuries and joint pain are common among linemen. Proper training and safety measures are essential to minimize these risks.
Below is a table summarizing the physical demands:
| Task | Physical Demand |
|---|---|
| Lifting Equipment | Heavy Weight |
| Climbing Structures | High Stamina |
| Working at Heights | Balance & Coordination |
| Prolonged Standing | Endurance |
Career Advancement
Career advancement for a Class A Lineman offers many opportunities. The role is critical in the power industry. Linemen can grow in their field with dedication and skills.
Specializations
Linemen can specialize in different areas. Specializations can lead to higher pay. Some linemen focus on transmission lines. Others may focus on distribution lines. Each specialization requires unique skills and training.
Here are some common specializations:
- Transmission Lineman: Works on high-voltage power lines.
- Distribution Lineman: Handles lower-voltage lines in neighborhoods.
- Substation Technician: Maintains and repairs electrical substations.
- Underground Lineman: Installs and maintains underground power lines.
Leadership Opportunities
Leadership roles offer another path for career growth. Experienced linemen can advance to supervisory roles. These roles include foreman and general foreman.
| Leadership Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Foreman | Leads a team of linemen on job sites. |
| General Foreman | Oversees multiple teams and job sites. |
| Project Manager | Manages large-scale projects and budgets. |
Leadership roles often come with added responsibilities. They also offer higher salaries and benefits.

Credit: www.southernwv.edu
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is A Class A Lineman?
A Class A lineman installs, repairs, and maintains electrical power systems. They work on high-voltage transmission lines. Their job involves climbing poles, operating heavy equipment, and ensuring safety standards. They play a crucial role in ensuring reliable electricity distribution.
What Is A Class C Lineman?
A Class C lineman installs, maintains, and repairs electrical power systems. They work on lower-voltage distribution lines. Their tasks include climbing poles, working with transformers, and ensuring electrical safety.
What Is The Highest Paid Type Of Lineman?
The highest-paid linemen are typically those working on high-voltage transmission lines. They often earn the most due to the job’s complexity and risk.
What Are The Two Types Of Lineman?
There are two types of linemen: offensive linemen and defensive linemen. Offensive linemen protect the quarterback and block for the running back. Defensive linemen focus on stopping the opposing team’s offensive plays.
Conclusion
A Class A Lineman plays a crucial role in maintaining our power infrastructure. Their skills ensure reliable electricity for all. Pursuing this career offers stability and growth opportunities. With dedication and training, you can thrive in this essential field. Consider becoming a Class A Lineman to make a significant impact.
