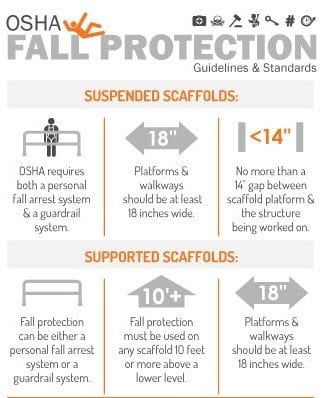
The OSHA Fall Protection Standard requires employers to provide fall protection at elevations of four feet in general industry workplaces. It also applies at six feet in the construction industry.
Falls are a leading cause of serious workplace injuries and deaths. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established the Fall Protection Standard to mitigate these risks. This standard mandates that employers implement fall protection systems for employees working at certain heights.
Compliance includes using guardrails, safety nets, or personal fall arrest systems. Proper training and equipment inspections are also required. By adhering to these guidelines, businesses can create safer work environments and reduce the likelihood of fall-related incidents. Protecting workers from falls is both a legal obligation and a moral imperative.
Credit: www.nac-hvac.com
Introduction To Osha Fall Protection
Falls are a leading cause of workplace injuries. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets standards to prevent falls. These standards protect workers from serious harm. Understanding OSHA fall protection is crucial for safety.
Importance Of Fall Protection
Fall protection saves lives. It reduces workplace injuries and fatalities. Proper fall protection ensures workers’ safety. It also minimizes workplace disruptions and costs due to accidents.
- Protects workers from serious injuries
- Reduces workplace accidents
- Minimizes costs associated with injuries
- Ensures compliance with safety regulations
Osha Regulations Overview
OSHA sets strict guidelines for fall protection. These regulations apply to various industries. They cover different types of fall hazards and control methods. Employers must provide fall protection when workers are exposed to fall hazards.
| Industry | Height Requirement | Fall Protection Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | 6 feet or more | Guardrails, Safety Nets, Personal Fall Arrest Systems |
| General Industry | 4 feet or more | Guardrails, Safety Nets, Personal Fall Arrest Systems |
| Shipyards | 5 feet or more | Guardrails, Safety Nets, Personal Fall Arrest Systems |
Employers must train workers on fall protection. They must ensure equipment is in good condition. Regular inspections are necessary to maintain safety standards.

Credit: resources.duralabel.com
Types Of Fall Hazards
Understanding the Types of Fall Hazards is crucial for workplace safety. Falls are a leading cause of serious injuries. Recognizing and mitigating these hazards can save lives.
Common Workplace Fall Risks
Workplaces present various fall risks. Some are more common than others. Here are a few:
- Slippery Surfaces: Wet floors can cause slips.
- Uneven Ground: Uneven surfaces can trip workers.
- Unprotected Edges: Open edges can lead to falls.
- Ladders: Improper use of ladders can be dangerous.
Identifying Potential Hazards
Identifying potential fall hazards is vital. Here are steps to help:
- Inspect the Work Area: Regularly check for risks.
- Use Safety Equipment: Ensure proper use of gear.
- Train Employees: Educate workers on safety.
- Report Hazards: Encourage reporting of dangers.
| Hazard Type | Description | Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Slippery Surfaces | Wet or oily floors | Use mats and signs |
| Uneven Ground | Rough or bumpy areas | Level the surface |
| Unprotected Edges | Open edges without rails | Install guardrails |
| Ladders | Misuse or damaged ladders | Inspect and use properly |
Fall Protection Systems
The OSHA Fall Protection Standard aims to prevent falls in the workplace. Fall protection systems are essential for worker safety. These systems include guardrails, safety nets, and personal fall arrest systems.
Guardrails And Safety Nets
Guardrails are barriers that prevent falls. They are installed on open sides of platforms and walkways. Guardrails consist of a top rail, midrail, and toeboard. The top rail must be 42 inches high. The midrail is placed halfway between the top rail and the floor. A toeboard is added at the bottom to prevent objects from falling.
Safety nets catch workers who fall. They are placed below the work area. Safety nets must be strong and regularly inspected. They should extend outward from the work area. The maximum drop distance allowed is 30 feet. Safety nets must be free of debris.
Personal Fall Arrest Systems
Personal fall arrest systems protect individual workers. These systems include a body harness, anchorage, and connecting device. The harness distributes fall forces over the body. The anchorage point must support 5,000 pounds per worker. Connecting devices include lanyards and lifelines. These devices limit the fall distance.
Workers must inspect their fall arrest systems before use. Damaged equipment must be replaced. Training is essential for proper use. Proper use reduces the risk of injury. Always follow manufacturer guidelines for safety.
Here is a quick comparison of the fall protection systems:
| System | Components | Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Guardrails | Top rail, midrail, toeboard | Regularly check for damage |
| Safety Nets | Netting, supports | Inspect for debris and damage |
| Fall Arrest Systems | Harness, anchorage, connecting device | Inspect before each use |
Fall protection systems save lives. Always ensure systems are in place and properly maintained. Safety is a priority for everyone.
Osha Compliance Requirements
Understanding OSHA’s fall protection standards is crucial for workplace safety. Employers must follow specific guidelines to protect workers from falls. Compliance with these standards helps prevent accidents and injuries.
Training And Education
Training and education are vital for fall protection. Workers must know how to use safety equipment properly.
- Provide training on how to use harnesses and lifelines.
- Ensure workers understand the risks of falls.
- Conduct regular refresher courses.
Employers should document all training sessions. This ensures compliance with OSHA requirements.
Inspection And Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of safety equipment are essential. This ensures equipment remains effective and safe.
| Inspection Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Check harnesses for wear and tear | Weekly |
| Inspect lifelines for damage | Monthly |
| Test anchor points | Quarterly |
Keep records of all inspections. This ensures ongoing compliance with OSHA standards.
Developing A Safety Plan
Creating a safety plan ensures workers are protected from falls. The OSHA Fall Protection Standard provides guidelines for safety. Developing a safety plan involves several key steps. These include risk assessment procedures and emergency response strategies.
Risk Assessment Procedures
Risk assessment procedures identify potential fall hazards. Follow these steps to conduct a proper risk assessment:
- Inspect the work area for hazards.
- Identify tasks that involve heights.
- Evaluate the likelihood of falls.
- Determine the potential severity of injuries.
Use a table to document findings:
| Task | Hazard | Likelihood | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Roof work | Unstable surface | High | Severe |
| Ladder use | Improper setup | Medium | Moderate |
Emergency Response Strategies
Having emergency response strategies is crucial. In case of a fall, follow these steps:
- Call emergency services immediately.
- Administer first aid if trained.
- Ensure the area is safe for responders.
- Document the incident for future review.
Train employees on emergency procedures regularly. Use drills to simulate real situations. This prepares everyone for actual emergencies.
Employee Responsibilities
Understanding employee responsibilities under the OSHA Fall Protection Standard is vital. Employees must follow safety protocols. They must also ensure their own safety and that of their coworkers. This section highlights key responsibilities.
Proper Use Of Equipment
Employees must use fall protection equipment correctly. This includes harnesses, lanyards, and guardrails. Proper use prevents accidents and injuries.
- Inspect equipment before each use for damages.
- Wear harnesses snugly to ensure they work.
- Attach lanyards to secure anchor points.
- Use guardrails around open edges and holes.
Reporting Unsafe Conditions
Employees must report unsafe conditions immediately. This includes broken equipment and hazardous work areas. Reporting keeps everyone safe.
Use the following steps to report issues:
- Identify the unsafe condition or hazard.
- Notify your supervisor or safety officer.
- Document the issue with photos or notes.
- Follow up to ensure the issue is resolved.
Reporting and using equipment correctly are key responsibilities. These actions save lives and prevent injuries.
Employer Responsibilities
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Fall Protection Standard mandates that employers must ensure the safety of their workers. Employers have specific responsibilities to minimize fall hazards. These responsibilities are critical to maintaining a safe work environment.
Providing Safety Gear
Employers must provide safety gear to all workers. This includes helmets, harnesses, and guardrails. Safety gear should be in excellent condition and regularly inspected.
- Helmets
- Harnesses
- Guardrails
Employers should also ensure the gear fits each worker properly. Poorly fitting gear can be dangerous and ineffective.
Ensuring Regular Training
Employers must ensure regular training for all employees. Training should cover how to use safety gear and recognize fall hazards. It should also include emergency procedures.
- How to use safety gear
- Recognize fall hazards
- Emergency procedures
Training should be provided at hiring, and at least once a year after that. Workers should also be retrained if job conditions change.
| Responsibility | Details |
|---|---|
| Providing Safety Gear | Helmets, harnesses, guardrails |
| Ensuring Regular Training | Initial and annual training |

Credit: www.bigrentz.com
Case Studies And Examples
Understanding OSHA’s Fall Protection Standard is crucial. Real-life case studies and examples help. They show how these standards save lives. Let’s explore some successful programs and lessons from workplace incidents.
Successful Fall Protection Programs
Many companies have implemented successful fall protection programs. Here are some examples:
| Company | Program Details | Results |
|---|---|---|
| XYZ Construction | Installed guardrails, safety nets, and harnesses. | Reduced fall incidents by 80% in one year. |
| ABC Manufacturing | Provided regular training and safety drills. | Zero fall-related injuries in the last two years. |
Lessons From Workplace Incidents
Workplace incidents teach us valuable lessons. Here are some examples:
- Incident 1: A worker fell from a scaffold.
- Lesson: Ensure all scaffolds are secure and inspected daily.
- Incident 2: An employee slipped on a wet floor.
- Lesson: Always mark wet areas with warning signs.
These examples highlight the importance of proper safety measures. Implementing OSHA’s Fall Protection Standards can prevent such incidents.
Future Of Fall Protection
The future of fall protection is exciting. New technologies and evolving regulations are shaping it. These changes will keep workers safer. Let’s explore what lies ahead.
Technological Innovations
Technological innovations are transforming fall protection. Smart harnesses are one example. They come with sensors to detect falls. These sensors alert emergency services immediately.
Drones are also becoming useful. They inspect work sites for safety issues. Drones reach places humans can’t. They help identify hazards quickly.
Virtual Reality (VR) training is another innovation. Workers can practice fall scenarios in a safe environment. VR makes training more effective and engaging.
Evolving Regulations
Evolving regulations ensure worker safety. New rules are always being developed. These rules adapt to modern work environments.
| Regulation | Impact |
|---|---|
| Increased fall protection requirements | More safety gear for workers |
| Regular safety audits | More frequent checks on safety measures |
| Mandatory VR training | Improved worker preparedness |
These regulations are important. They ensure that safety standards keep up with new technologies. This makes work environments safer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Osha Standard For Fall Protection Systems?
The OSHA standard for fall protection systems requires protection at elevations of 4 feet in general industry. For construction, it’s 6 feet. Employers must provide guardrails, safety nets, or personal fall arrest systems to prevent falls. Proper training and equipment are essential for compliance.
What Is The Osha 4ft Rule?
The OSHA 4ft rule mandates fall protection for workers at heights of 4 feet or more in general industry. This includes guardrails, safety nets, or personal fall arrest systems to prevent injuries from falls. Compliance ensures workplace safety and reduces accident risks.
What Are The Osha Free Fall Requirements?
OSHA requires fall protection for workers at heights of 4 feet in general industry. For construction, it’s 6 feet.
How Long Is Osha Fall Protection Good For?
OSHA fall protection equipment typically lasts 5 years. Always inspect gear before use and follow manufacturer guidelines for lifespan.
Conclusion
Ensuring compliance with OSHA fall protection standards is crucial for workplace safety. Prioritize training and proper equipment. Safe practices prevent accidents and save lives. Stay updated with OSHA regulations to maintain a secure environment. Investing in fall protection measures benefits both employees and employers.
Safety should always be a top priority.

