A 120/240 transformer bank steps down high voltage to 120 and 240 volts. It’s commonly used in residential and small commercial applications.
A 120/240 transformer bank is essential for distributing power in homes and small businesses. It converts high voltage from power lines to safer, usable levels of 120 and 240 volts. This ensures that electrical systems can run efficiently and safely.
Many appliances and devices rely on this voltage conversion for proper operation. The transformer bank typically consists of two or more transformers working together to provide the necessary voltage levels. Understanding its role can help you better manage electrical systems and improve energy efficiency. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure longevity and reliability.
Introduction To 120/240 Transformer Bank
A 120/240 Transformer Bank is vital for power distribution. It converts high voltage to a usable level. This allows safe electricity for homes and businesses. Understanding its purpose and applications is essential.
Purpose And Importance
The main purpose of a 120/240 Transformer Bank is voltage conversion. It ensures that electricity is safe for use. High voltage is dangerous for everyday devices. The transformer bank reduces this risk.
Its importance cannot be overstated. Without it, many electrical devices would not function. This equipment protects appliances from damage. It also enhances the safety of electrical systems.
Common Applications
The 120/240 Transformer Bank has various applications. It is commonly found in residential areas. It powers homes by converting high voltage to 120/240V.
Another application is in commercial buildings. These transformers support businesses with safe electricity. They are also used in small industries. This allows machinery to operate efficiently.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Residential Areas | Provides safe voltage for household devices. |
| Commercial Buildings | Ensures safe power for business operations. |
| Small Industries | Enables efficient operation of machinery. |

Credit: www.eng-tips.com
Basic Components
A 120/240 transformer bank is essential in electrical systems. It converts voltages between 120V and 240V. The basic components include the core material and windings. Understanding these parts helps in maintaining and troubleshooting the transformer.
Core Material
The core material is crucial for transformer efficiency. It typically consists of laminated steel. This reduces energy losses due to hysteresis and eddy currents. Laminated steel is stacked together. This enhances the transformer’s magnetic properties. The core is designed to minimize energy loss. Core material choice affects the transformer’s performance.
Windings
The windings are made of copper or aluminum wire. Copper windings are more efficient. Aluminum windings are lighter and cheaper. The windings wrap around the core. They create magnetic fields when current flows through them. Windings are divided into primary and secondary types.
| Type of Winding | Material | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Primary | Copper or Aluminum | Receives input voltage |
| Secondary | Copper or Aluminum | Delivers output voltage |
The number of turns in the windings determines the voltage transformation. More turns in the secondary winding increase the output voltage. Fewer turns reduce it. Proper insulation is vital for windings. This prevents short circuits and ensures safety.
- Primary Windings: Connect to the input voltage source.
- Secondary Windings: Connect to the output load.
- Insulation: Keeps the windings safe and efficient.
Understanding the core material and windings is essential. It helps in maintaining the 120/240 transformer bank. This knowledge ensures efficient and safe operation.
Working Principle
The working principle of a 120/240 Transformer Bank is fundamental to electricity distribution. This transformer bank is crucial for stepping down high voltage to usable levels. It ensures safe and efficient power delivery to homes and businesses.
Voltage Transformation
The primary function is voltage transformation. The transformer bank converts high voltage to lower, safer levels. The primary winding receives high voltage and the secondary winding delivers reduced voltage. This step-down is essential for everyday electrical appliances.
Here’s a simple table to illustrate the voltage transformation:
| Input Voltage (Primary) | Output Voltage (Secondary) |
|---|---|
| 7200V | 120V / 240V |
Phase Relationships
Understanding phase relationships is key for transformer banks. A 120/240 transformer bank typically operates on a single-phase system. The primary winding is connected in a way to maintain phase integrity. The secondary winding is split into two equal voltages. This split allows for both 120V and 240V outputs.
Key points on phase relationships:
- Single-phase operation
- Primary winding maintains phase
- Secondary winding splits voltage
This splitting ensures proper phase balance and voltage supply. It allows for versatile electrical applications.
Installation Guidelines
Installing a 120/240 Transformer Bank requires careful planning and adherence to safety standards. Proper installation ensures efficient operation and longevity of the equipment. Follow these guidelines to ensure a successful setup.
Site Selection
Choosing the right site for your transformer bank is crucial. Ensure the site is level and stable. Avoid areas prone to flooding or excessive moisture. The location should have adequate ventilation to prevent overheating.
Consider the proximity to the load center. A shorter distance reduces voltage drop. Ensure the site is accessible for maintenance and emergency services.
Safety Precautions
Safety is paramount during installation. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). This includes gloves, safety glasses, and hard hats.
De-energize all circuits before beginning the installation. Use a multimeter to confirm zero voltage. Keep a first-aid kit and fire extinguisher on site.
Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for grounding. Proper grounding prevents electrical shocks and ensures system stability.
Installation Steps
- Position the transformer bank on a stable platform.
- Connect the primary and secondary windings as per the wiring diagram.
- Tighten all connections securely to prevent loose contacts.
- Install the grounding system as specified.
- Test the installation with appropriate testing equipment.
Adhering to these installation guidelines ensures a safe and efficient setup of your 120/240 Transformer Bank. Proper site selection and safety precautions are key to a successful installation.
Performance Optimization
Optimizing the performance of a 120/240 Transformer Bank is crucial. It ensures efficiency and reliability. This section covers key strategies.
Load Balancing
Load balancing is vital for transformer longevity. Unbalanced loads stress the transformer.
- Monitor load distribution regularly.
- Use a load balancing tool.
- Check for overheating signs.
Balanced loads enhance transformer performance. They also reduce maintenance costs.
Efficiency Tips
Improving efficiency saves energy and costs. Here are some tips:
- Keep connections tight and clean.
- Regularly inspect and maintain the transformer.
- Use energy-efficient devices and appliances.
Small changes can lead to significant energy savings. They also extend the transformer’s life.
| Tip | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Keep connections tight | Reduces energy loss |
| Regular inspections | Identifies issues early |
| Energy-efficient devices | Lower energy consumption |
Maintenance Practices
Proper maintenance ensures the longevity and efficiency of your 120/240 Transformer Bank. Regular checks and timely troubleshooting are crucial. Effective maintenance practices prevent costly repairs and downtime. Below are key maintenance practices to follow.
Routine Inspections
Routine inspections are essential for your transformer bank. Inspect components for physical damage. Check for signs of wear and tear. Look for any oil leaks in the system. Verify that all connections are secure. Inspect the cooling system for blockages. Ensure the safety devices are functioning properly.
Use the table below to track your inspection schedule:
| Inspection Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Check for physical damage | Monthly |
| Inspect oil levels | Quarterly |
| Verify connections | Annually |
| Test safety devices | Annually |
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting helps identify issues before they escalate. Here are steps for effective troubleshooting:
- Identify any unusual noises or vibrations.
- Check for overheating or unusual temperature changes.
- Look for electrical faults or tripping circuits.
- Examine oil for discoloration or contamination.
- Monitor voltage levels for irregularities.
If you find any issues, take immediate action. Consult the manufacturer’s guide for specific troubleshooting steps.
Remember, consistent maintenance is key to a reliable transformer bank.
Cost Considerations
Understanding the cost implications of a 120/240 transformer bank is crucial. This section dives into the initial investment and operational costs, helping you make informed decisions.
Initial Investment
The initial investment for a 120/240 transformer bank includes several factors. Here’s a breakdown:
| Item | Cost |
|---|---|
| Transformer Unit | $2,000 – $5,000 |
| Installation | $500 – $1,500 |
| Permits and Licensing | $200 – $500 |
Transformer Unit costs depend on the brand and specifications. Installation costs vary by location and complexity. Permits and Licensing fees are essential and usually required by local authorities.
Operational Costs
Operational costs include maintenance, energy consumption, and potential repairs:
- Maintenance: Regular inspections and servicing can cost $100 – $300 annually.
- Energy Consumption: The efficiency of the transformer affects your energy bills. A more efficient transformer can save money in the long run.
- Repairs: Unexpected repairs can range from $200 to $1,000. Keeping a maintenance schedule reduces these costs.
Understanding these costs helps you budget effectively. Over time, efficient maintenance and energy usage can reduce your overall expenses.

Credit: www.reddit.com
Future Trends
The world of transformers is evolving rapidly. The future of the 120/240 Transformer Bank is looking promising. With new technologies and a focus on sustainability, exciting trends are emerging.
Technological Advances
Technological advances are changing how transformers work. Smart transformers are becoming more common. These transformers use digital sensors to monitor performance. They can also adjust settings automatically.
Another trend is the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI). AI can predict issues before they happen. This helps to reduce downtime and improve efficiency. Wireless technology is also being integrated. This allows for real-time monitoring and control.
Sustainability
Sustainability is a big focus for the future. Eco-friendly materials are being used more. These materials are better for the environment. They also make transformers more durable.
Energy efficiency is another key trend. High-efficiency transformers are designed to use less energy. This helps to reduce carbon footprints. The use of renewable energy sources is also increasing. Solar and wind power are being used to power transformers.
| Technological Advances | Sustainability |
|---|---|
| Smart Transformers | Eco-friendly Materials |
| Artificial Intelligence | High-efficiency Transformers |
| Wireless Technology | Renewable Energy Sources |
The future of the 120/240 Transformer Bank is bright. New technologies and sustainability efforts are key trends to watch.
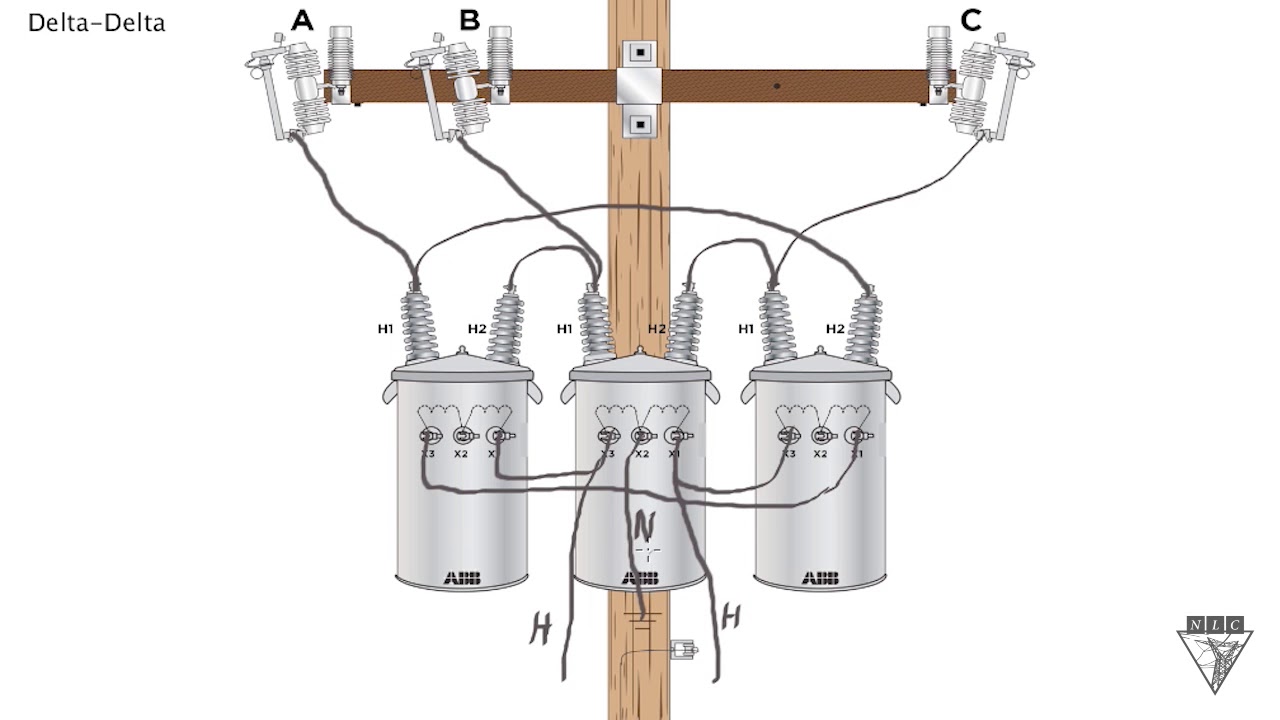
Credit: m.youtube.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Does 120 240v Mean Transformer?
A 120/240V transformer provides two voltage options, 120V and 240V, for different electrical devices. It ensures compatibility and efficiency.
What Should The High Leg Voltage Be On A 120 240 Volt Delta Connected Transformer Secondary?
The high leg voltage on a 120/240 volt delta connected transformer secondary should measure 208 volts. This ensures proper functionality.
What Is Transformer Bank Used For?
A transformer bank converts electrical energy between different voltage levels, ensuring efficient power distribution and transmission.
What Is The Voltage Of A Closed Delta Bank?
The voltage of a closed delta bank is typically the same as the line voltage of the system. For a 480V system, the closed delta bank voltage is 480V.
Conclusion
Understanding the 120/240 transformer bank is crucial for efficient power distribution. This knowledge helps optimize energy use. Proper maintenance and installation ensure longevity and reliability. Investing in quality transformers can lead to significant energy savings. Stay informed and make smart decisions for your electrical needs.

